Telecommunications Equipment Career Path: Opportunities, Challenges, and Growth Potential
Telecommunications equipment as a career path: an overview
The telecommunications equipment sector represents a vital component of our modern connected world. This industry encompass the design, manufacture, installation, and maintenance of the hardware that enable communication across distances. For those consider their professional future, telecommunications equipment offer a compelling career path with diverse opportunities and substantial growth potential.
The global telecommunications equipment market continues to expand, drive by increase connectivity demands, 5 g implementation, and the internet of things( IOT) revolution. This growth translate straight into career opportunities for individuals with the right skills and interests.
Key job roles in telecommunications equipment
The telecommunications equipment field offer numerous specialized positions that cater to different skills and interests:
Technical roles
-
Telecommunications equipment installer:
Responsible for set up and configure hardware such as routers, switches, and transmission equipment. -
Rf (radio frequency )engineer:
Designs and optimize wireless networks, focus on signal propagation and coverage. -
Network infrastructure engineer:
Plans and implement telecommunications networks, ensure reliability and performance. -
Hardware engineer:
Develops and test new telecommunications equipment and components. -
Field service technician:
Troubleshoots and repairs telecommunications equipment at customer sites.
Management and support roles
-
Telecommunications project manager:
Oversees equipment installation projects, coordinate teams and resources. -
Technical sales representative:
Sell telecommunications equipment to businesses and service providers. -
Network operations center (nnot)technician:
Monitors network performance and respond to technical issues. -
Telecommunications consultant:
Advise organizations on equipment selection and network design.
Educational requirements and pathways
Entry into the telecommunications equipment field typically require some formal education, though requirements vary by position:
Technical certifications
Industry certifications provide specialized knowledge and enhance employability:
- Compton network+
- Cisco certified network associate (cCCNA)
- Certified telecommunications network specialist (ccans)
- Fiber optics installer certification
- Vendor specific certifications from companies like Nokia, Ericsson, and Huawei
Degree programs
Higher level positions frequently require college degrees:
- Associate’s degree in electronics technology or telecommunications technology
- Bachelor’s degree in electrical engineering, computer engineering, or telecommunications
- Master’s degree for advanced research and development positions
Entry points
Many professionals enter the field through:

Source: zippia.com
- Technical school programs
- Apprenticeships with telecommunications companies
- Military training in communications systems
- Entry level positions with on the job training
Salary potential and compensation
Telecommunications equipment careers typically offer competitive compensation, with salaries vary base on role, experience, location, and employer:
Entry level positions
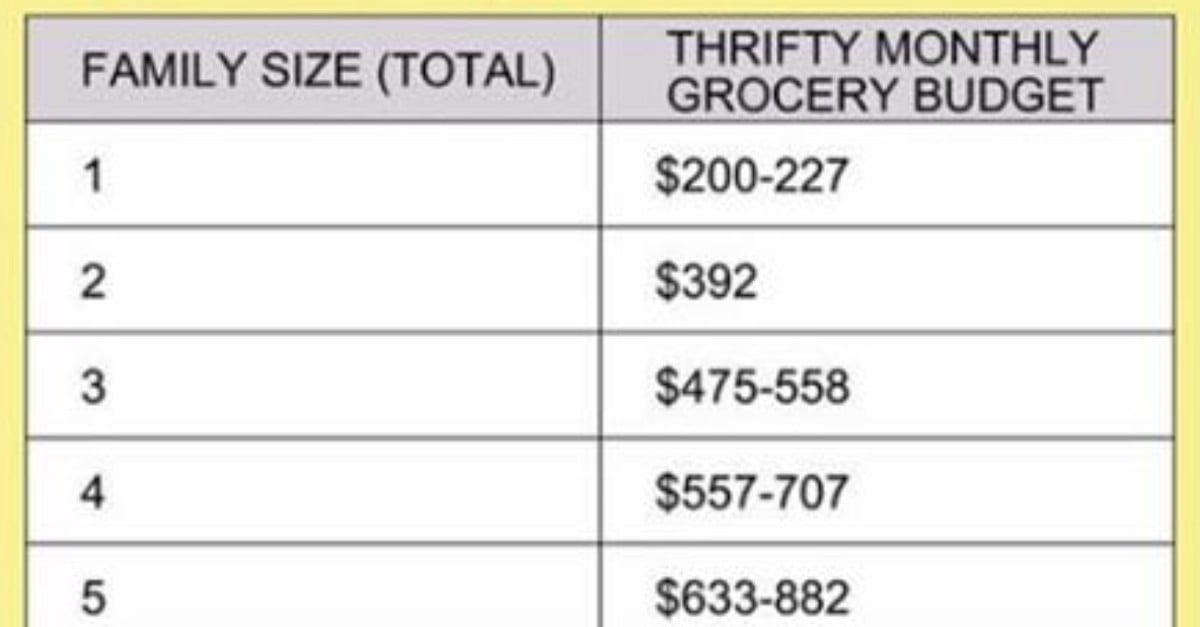
Telecommunications equipment installers and technicians typically start with salaries range from $40,000 to $$55000 yearly. These positions oftentimes include opportunities for overtime pay and performance bonuses.
Mid-career professionals
With 5 10 years of experience, professionals can expect to earn $60,000 to $$85000 yearly in roles such as senior technicians, network engineers, and project coordinators.
Senior and specialized roles
Rf engineers, network architects, and telecommunications managers can earn $85,000 to $$120000 + depend on their expertise and responsibilities.
Additional compensation
Beyond base salary, telecommunications equipment professionals oft receive:
- Health insurance and retirement benefits
- Pay training and certification programs
- Vehicle allowances or company vehicles for field positions
- Mobile phone allowances
- Performance bonuses
Industry growth and job outlook
The telecommunications equipment sector offer promise long term career prospects due to several factors:
Technology drivers
Several technological trends continue to fuel demand for skilled professionals:
-
5 g network deployment:
The ongoing rollout of fifth generation wireless technology require extensive equipment installation and optimization. -
Fiber optic expansion:
Increase demand for high speed internet drive fiber optic network development. -
IOT growth:
The proliferation of connect devices necessitate robust telecommunications infrastructure. -
Network security:
Grow cybersecurity concerns create demand for secure telecommunications equipment. -
Rural connectivity initiatives:
Government back programs to expand broadband access create additional job opportunities.
Job stability
Telecommunications equipment careers offer comparatively high job security for several reasons:
- Essential infrastructure status protect many positions during economic downturns
- Physical equipment require on site maintenance that can not be full automate
- Continuous technology evolution create ongoing demand for skilled workers
- Telecommunications services remain necessary disregarding of economic conditions
Advantages of a telecommunications equipment career
This career path offer numerous benefits that make it attractive to many professionals:
Technical engagement
For those who enjoy work with technology, telecommunications equipment offer:
- Hands-on experience with cutting edge hardware
- Problem solve opportunities in complex systems
- Exposure to both establish and emerge technologies
- Opportunities to work with diverse equipment types
Career mobility
The telecommunications equipment field provides excellent career advancement potential:
- Clear progression paths from entry level to specialist roles
- Opportunities to move between technical and management tracks
- Transferable skills that apply across various industries
- Global job opportunities with multinational equipment manufacturers
Work environment variety
Professionals can choose from diverse work settings:
- Field base roles for those who enjoy work outside and in different locations
- Laboratory positions for those prefer control environments
- Office base engineering and design roles
- Remote monitoring and support positions
Challenges in telecommunications equipment careers
While offer many advantages, this career path besides present certain challenges:

Source: goxfinity.com
Technical demands
The field require continuous learning and adaptation:
- Rapid technological changes necessitate ongoing education
- Complex systems require extensive technical knowledge
- Troubleshooting skills must be continually refined
- Multiple certification renewals may be necessary
Physical requirements
Many roles involve physical demands:
- Tower climbs for wireless equipment installation and maintenance
- Heavy equipment handling
- Work in challenge weather conditions
- Confine space entry for some installation scenarios
Schedule considerations
Work schedules can be demand:
- On call rotations for emergency repairs
- Overnight work during maintenance windows
- Weekend installations to minimize business disruptions
- Travel requirements for field positions
Skills for success in telecommunications equipment
To thrive in this field, professionals should develop specific technical and soft skills:
Technical skills
-
Network protocols:
Understand TCP / IP, Ethernet, and wireless protocols -
Equipment configuration:
Set up routers, switches, and transmission equipment -
Troubleshoot:
Diagnose and resolve hardware and connectivity issues -
Cable management:
Install and organize copper and fiber optic cabling -
Test equipment operation:
Use spectrum analyzers, network testers, and other diagnostic tools
Soft skills
-
Problem-solving:
Approach complex issues methodically -
Communication:
Explain technical concepts to non-technical stakeholders -
Teamwork:
Collaborate on large scale installations and projects -
Attention to detail:
Ensure precise equipment configuration -
Time management:
Meeting installation deadlines and maintenance schedules
Break into the telecommunications equipment field
For those interested in pursue this career path, several strategies can help secure that first position:
Education and training
Focus on relevant education:
- Pursue telecommunications specific programs at technical schools
- Obtain foundational certifications like Compton network+
- Complete hands-on training programs with equipment manufacturers
- Participate in internships with telecommunications companies
Network opportunities
Connect with industry professionals:
- Join telecommunications industry associations
- Attend trade shows and technical conferences
- Participate in online forums and communities
- Connect with professionals on LinkedIn and other platforms
Entry level positions
Consider these starting points:
- Cable installer or technician
- Help desk support for telecommunications systems
- Equipment testing and quality control
- Telecommunications equipment warehouse and inventory roles
Future trends in telecommunications equipment careers
The field continue to evolve, with several emerge trends create new opportunities:
Convergence with it
Telecommunications and information technology are progressively overlapping, create roles that require knowledge of both domains:
- Network function virtualization specialists
- Software define network engineers
- Cloud base telecommunications infrastructure experts
Smart infrastructure
The integration of telecommunications with smart city initiatives create new career paths:
- Smart grid communications specialists
- Intelligent transportation systems technicians
- Public safety network engineers
Specialized growth areas
Several niche sectors are experience rapid growth:
- Private 5 g network implementation for enterprises
- Satellite communications equipment for global connectivity
- Emergency communications systems
- Industrial IOT network infrastructure
Is telecommunications equipment right for you?
This career path may be specially intimately suited for individuals who:
- Enjoy work with hardware and physical systems
- Have strong problem solve abilities
- Prefer careers with clear advancement paths
- Are comfortable with continuous learning
- Appreciate the combination of technical challenges and practical applications
Telecommunications equipment offer a stable career with competitive compensation and diverse opportunities. While it requires technical aptitude and ongoing education, itprovidese the satisfaction of build and maintain the critical infrastructure that connect our world.
For those with the right combination of technical interest, problem solve ability, and willingness to learn, telecommunications equipment represent not but a job but a long term career path with substantial rewards and growth potential.
MORE FROM jobsmatch4u.com