Macro Environment: Complete Guide to External Business Forces
Understand the macro environment
The macro environment represent the broader external forces that influence businesses, industries, and entire economies. These powerful factors operate beyond any single company’s control yet importantly impact strategic decisions, market opportunities, and long term success.
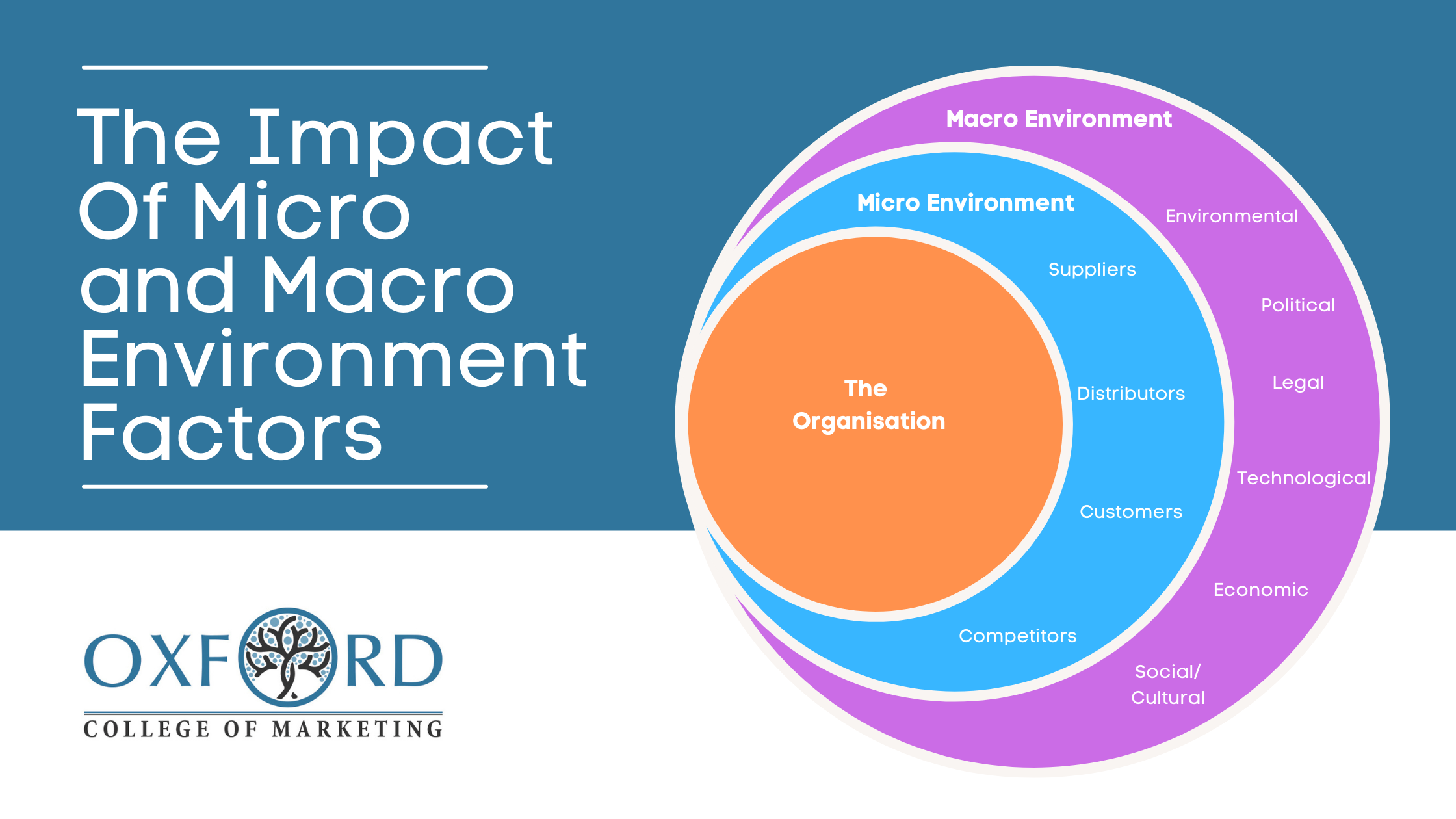
Unlike the micro environment, which include direct stakeholders like customers, suppliers, and competitors, the macro environment encompasses sweeping societal trends and conditions. These forces create the backdrop against which all business activities unfold, make their understanding essential for effective planning andecision-makingng.
The six key components of macro environment
Business analysts usually use the pestle framework to examine macro environmental factors consistently. This comprehensive approach ensures no critical external force go unnoticed.
Political factors
Political stability, government policies, and regulatory changes form the foundation of the macro environment. These elements include tax policies, trade regulations, labor laws, and political stability. Companies operate internationally must navigate vary political landscapes, each present unique challenges and opportunities.
Government spend priorities influence entire sectors. Infrastructure investments boost construction and engineering firms, while healthcare policy changes affect pharmaceutical and medical device companies. Political tensions between nations can disrupt supply chains and create new market barriers nightlong.
Economic conditions
Economic factors represent peradventure the virtually instantly visible macro environmental forces. Interest rates, inflation, unemployment levels, and economic growth rates instantly impact consumer spending power and business investment decisions.
During economic expansion, consumers spend more freely, create opportunities for luxury goods and discretionary services. Conversely, economic downturns shift demand toward essential products and value orient offerings. Exchange rates affect international trade, make exports more or less competitive in global markets.
Economic indicators serve as early warning systems for businesses. Rise inflation signal potential cost increases, while decline unemployment suggest stronger consumer demand beforehand.
Social and cultural trends
Demographic shifts, cultural values, lifestyle changes, and social attitudes create powerful currents in the macro environment. Age populations in develop countries drive healthcare and senior services demand, while younger demographics fuel technology adoption and social media engagement.
Cultural values evolve unendingly, influence consumer preferences and expectations. Environmental consciousness has transformed multiple industries, from automotive to fashion. Health and wellness trends reshape food production, retail offerings, and workplace policies.
Social movements can quickly alter market dynamics. The push for diversity and inclusion affects hire practices, marketing strategies, and corporate governance across industries.
Technological advancement
Technology represent one of the virtually dynamic macro environmental forces. Digital transformation, artificial intelligence, automation, and emerge technologies unendingly reshape competitive landscapes and create new business models.
Technological disruption can eliminate entire industries while create others. Digital photography destroy traditional film companies but birth new imaging technologies and social media platforms. Cloud compute transform software delivery and enable remote work capabilities.
The pace of technological change accelerates endlessly, make adaptability crucial for survival. Companies must balance invest in current technologies while prepare for future innovations.
Legal and regulatory framework
Laws, regulations, and compliance requirements form critical macro environmental constraints and opportunities. Industry specific regulations, consumer protection laws, and international trade agreements shape operational possibilities.
Regulatory changes can create competitive advantages for prepared companies while disadvantage others. Environmental regulations favor clean technology companies but challenge traditional manufacturing. Data privacy laws affect technology companies’ business models and operational procedures.
Legal trends oftentimes follow social movements, translate cultural shifts into formal requirements. Understand regulatory directions help companies prepare for compliance challenges and identify emerge opportunities.
Environmental factors
Climate change, natural disasters, resource availability, and environmental regulations progressively influence business operations. Supply chain disruptions from extreme weather events affect global commerce, while resource scarcity drive innovation in materials and processes.
Environmental considerations extend beyond compliance to strategic opportunities. Companies develop sustainable solutions oftentimes gain competitive advantages and access to environmentally conscious market segments.
Geographic factors within the environmental category include location specific challenges like natural disaster risks, climate conditions, and resource availability that affect operational decisions.
How macro environment impact business strategy
Successful companies integrate macro environmental analysis into strategic planning processes. These external forces influence market opportunities, competitive dynamics, and operational requirements in predictable patterns.
Market opportunity identification
Macro environmental trends reveal emerge market opportunities before they become obvious to competitors. Demographic shifts signal change demand patterns, while technological advances create new product possibilities.
Companies monitor macro trends can position themselves well. The age population trend create opportunities in healthcare technology, home modification services, and senior focused financial products yearn before these markets become crowded.
Risk management and mitigation
Understand macro environmental forces enable proactive risk management. Political instability warnings help companies diversify supply chains, while economic indicators guide inventory and investment decisions.
Scenario planning base on macro environmental analysis prepare organizations for various futures. Companies develop contingency plans for different economic conditions, regulatory changes, or technological disruptions.
Competitive positioning
Macro environmental forces affect all industry participants, but companies respond otherwise base on their capabilities and strategies. Understand these forces help predict competitor actions and identify differentiation opportunities.
Regulatory changes oftentimes favor companies with specific capabilities or resources. Environmental regulations benefit companies with clean technologies, while trade restrictions may advantage domestic producers over international competitors.
Analyze macro environmental trends
Effective macro environmental analysis require systematic approaches and reliable information sources. Organizations must develop capabilities to monitor, interpret, and respond to external changes.
Information gathering and sources
Multiple information sources provide insights into macro environmental trends. Government statistics, industry reports, academic research, and news media offer different perspectives on emerge changes.
International organizations like the World Bank, International Monetary Fund, and United Nations publish comprehensive reports on global trends. Industry associations provide sector specific analysis, while consulting firms offer strategic interpretations of macro trends.
Primary research through customer surveys, expert interviews, and market studies provide organization specific insights into how macro trends affect particular businesses or industries.
Trend analysis techniques
Quantitative analysis identify patterns in macro environmental data. Time series analysis reveal trends in economic indicators, demographic statistics, and technological adoption rates. Statistical modeling help predict future conditions base on historical patterns.
Qualitative analysis interpret the meaning and implications of macro trends. Expert judgment, scenario development, and cross impact analysis explore how different macro factors interact and influence each other.

Source: collidu.com
Combine quantitative and qualitative approaches provide comprehensive understanding. Numbers reveal what’s happen, while qualitative analysis explain why and explore potential implications.
Respond to macro environmental changes
Recognition of macro environmental forces mean little without effective response strategies. Organizations must develop capabilities to adapt rapidly and capitalize on external changes.
Strategic flexibility
Successful companies build flexibility into their strategies and operations. Diversified revenue streams, adaptable business models, and scalable operations enable rapid responses to macro environmental changes.
Financial flexibility through strong balance sheets and access to capital provide options during uncertain times. Operational flexibility through modular processes and cross train workforce enable quick pivots when conditions change.
Innovation and adaptation
Macro environmental changes oftentimes require new solutions, create innovation opportunities. Companies that develop relevant capabilities other gain competitive advantages as trends accelerate.
Innovation strategies should align with macro trends instead than fight against them. Technology companies embrace artificial intelligence trends position themselves advantageously than those resist change.
Common macro environment challenge
Organizations face predictable challenges when deal with macro environmental forces. Understand these difficulties help develop more effective response strategies.
Information overload
The volume of available information about macro trends can overwhelm decision makers. Organizations must develop filter mechanisms to focus on the virtually relevant factors for their specific situations.
Prioritization frameworks help identify which macro factors deserve the most attention. Companies should focus on trends with high impact probability and significant potential effects on their operations.
Uncertainty and prediction difficulties
Macro environmental forces are inherently unpredictable in their timing and magnitude. Political events, economic cycles, and technological breakthroughs oftentimes surprise eventide expert observers.
Sooner than will try to will predict precisely when changes will occur, successful companies will prepare for multiple scenarios. Robust strategies work sensibly advantageously across different possible futures instead than optimize for single predict outcomes.
Building macro environmental awareness
Organizations must develop systematic capabilities for monitoring and respond to macro environmental changes. This requires dedicated resources, appropriate processes, and cultural commitment to external awareness.
Organizational capabilities
Environmental scan capabilities enable continuous monitoring of macro trends. Some companies establish dedicated strategic planning units, while others distribute scan responsibilities across different functional areas.
Cross-functional teams oftentimes provide the best macro environmental analysis because different perspectives reveal various implications of external changes. Marketing teams understand customer implications, while operations teams grasp supply chain effects.

Source: blog.oxfordcollegeofmarketing.com
Integration with decision-making
Macro environmental analysis must connect to actual decision make processes to create value. Regular strategy reviews should incorporate update environmental assessments, and major decisions should consider macro trend implications.
Communication systems should disseminate relevant macro environmental insights throughout the organization. Front line employees oftentimes observe early signals of macro changes through customer interactions and operational experiences.
The macro environment represents a complex web of external forces that shape business conditions and opportunities. Companies that develop sophisticated understanding of these forces and build adaptive capabilities position themselves for long term success. While no organization can control macro environmental factors, those that monitor, interpret, and respond efficaciously to external changes systematically outperform competitors who ignore or misunderstand these powerful influences.
MORE FROM jobsmatch4u.com